How to manufacture a plate heat exchanger?
Release time:
2025-01-14
The plate heat exchanger is an efficient and compact heat exchange device. Its manufacturing process includes multiple steps from raw material selection to whole machine assembly. How work a plate heat exchanger? The following is a detailed manufacturing process:
1. Plate manufacturing
1.1.Material selection
1.1.1.Common materials:
Stainless steel (such as 304, 316L): Good corrosion resistance and thermal conductivity, suitable for general industrial use.

1.1.2.Titanium alloy: Strong corrosion resistance, suitable for highly corrosive environments (such as seawater).
1.1.3.Hastelloy or nickel-based alloy: Used in extremely corrosive or high temperature environments.
1.2. Plate forming
1.2.1.Stamping:
Use a hydraulic press or mechanical punch to press a metal plate into a plate with a specific corrugated structure.
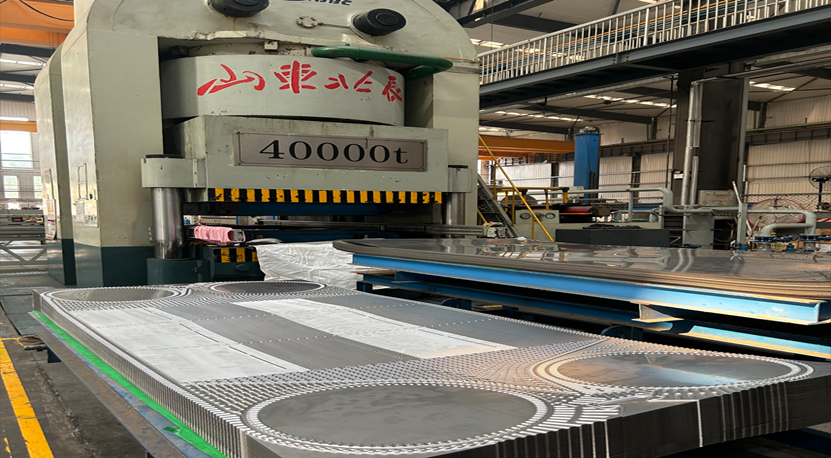

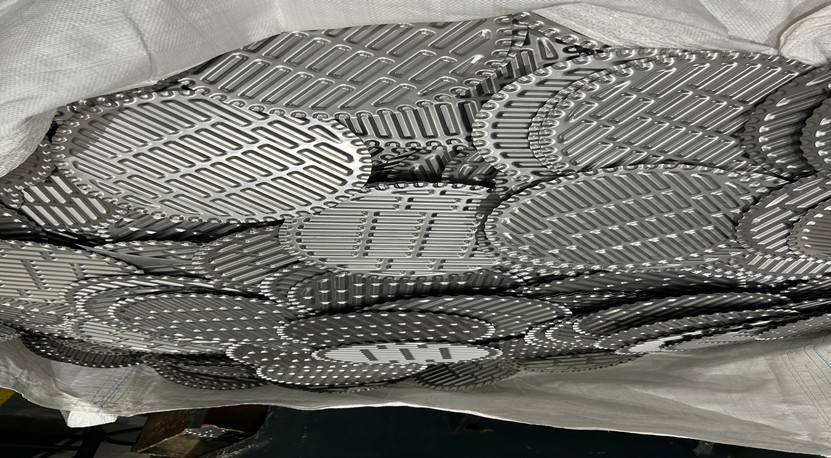
1.2.2.Corrugation type: oblique corrugation, herringbone corrugation, sinusoidal corrugation, etc., selected according to fluid characteristics.
1.2.3.Function: Increase heat transfer area and enhance turbulence effect.
1.2.4.Trimming and punching:
Trimming: Ensure that the edges of the plate are flat for easy assembly.
Punching: Punch holes on the top and bottom of the plate to align the channels of hot and cold fluids.

1.3.Surface treatment
1.3.1.Remove the oxide layer: Clean the oxide on the surface of the plate by pickling or sandblasting.
1.3.2.Polishing: Improve the surface finish of the plate and reduce dirt adhesion.
2. Production of sealing gaskets
2.1. Material selection
2.1.1.Select different types of rubber materials according to the working environment:
EPDM (ethylene propylene rubber): Suitable for high temperature or low corrosive fluids.
2.1.2.Fluororubber (Viton): Suitable for high temperature and highly corrosive fluids.
2.1.3.NBR (nitrile rubber): Suitable for oily fluids.
2.2. Gasket molding
Use molds to manufacture gaskets through injection molding or compression molding to ensure contact accuracy with the plate.
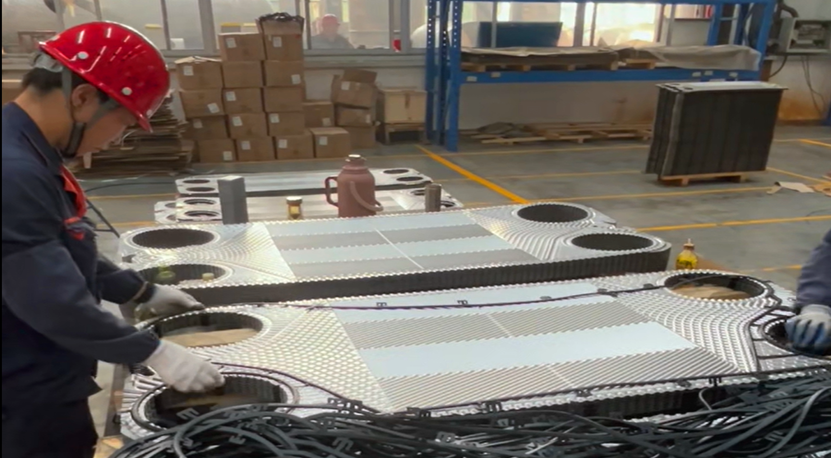

2.3. Pretreatment
Clean the surface of the sealing gasket to ensure no contamination during installation.
3. Frame manufacturing
3.1. Material processing
3.1.1.Frame material:
Carbon steel (surface sprayed with anti-corrosion coating) or stainless steel.
3.1.2.Cutting and welding: Cut and weld the metal plates into frame components according to the design drawings.
3.2. Production of movable and fixed pressure plates
Made of thick steel plates, machined to ensure flatness and strength.
Bolt holes are opened on the pressure plates to install and fix the plate components.
3.3.Surface treatment
3.3.1.Carbon steel frame: Spray anti-corrosion coating (such as epoxy coating).
3.3.2.Stainless steel frame: Polished to increase aesthetics and corrosion resistance.
4. Assembly process
4.1.Plate assembly
The plates are arranged alternately according to hot and cold fluids.
Sealing gaskets are installed on the edge of each plate to ensure that the fluid flows in the flow channel without leakage.
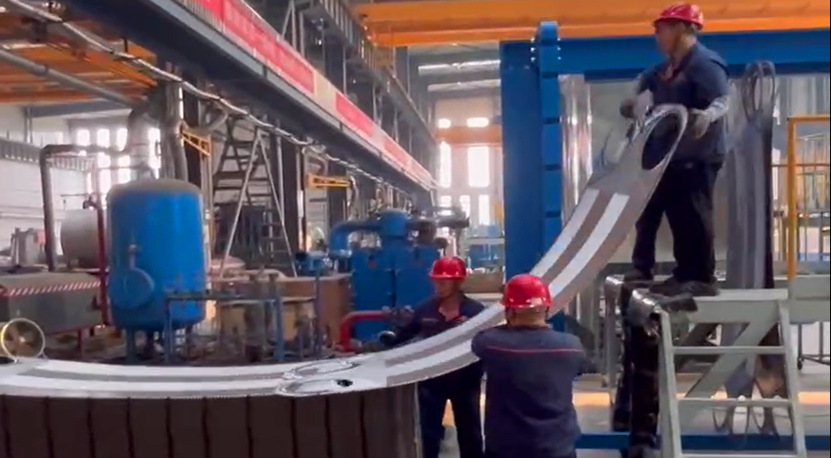

4.2. Frame assembly
The plate assembly is clamped between the fixed pressure plate and the movable pressure plate.
Uniform pressure is applied by tightening the bolts to form a good seal between the plate and the gasket.
4.3.Interface installation
Install the inlet and outlet joints of the hot and cold fluids on the frame to ensure reliable connection with the pipeline system.
5. Quality Inspection
5.1. Sealing Test
Inject high-pressure water or gas for leakage test to check the sealing performance.
5.2. Pressure Test
Apply the design pressure to the equipment under simulated working conditions to test its structural strength and pressure resistance.
5.3.Performance Test
Check whether the heat exchange efficiency meets the design requirements to ensure the reliable performance of the equipment.
6. Packaging and Delivery
6.1. Cleaning and Packaging
After completing the quality inspection, clean and pack the equipment.
Rust-proof treatment or vacuum packaging is performed on the exported equipment.
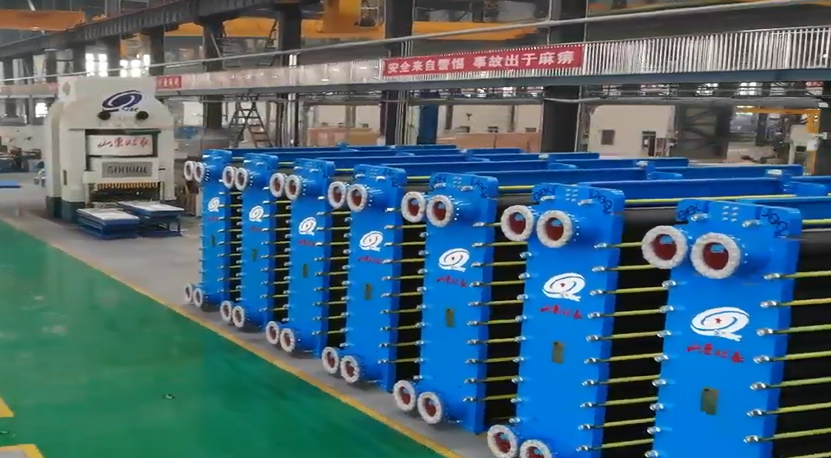

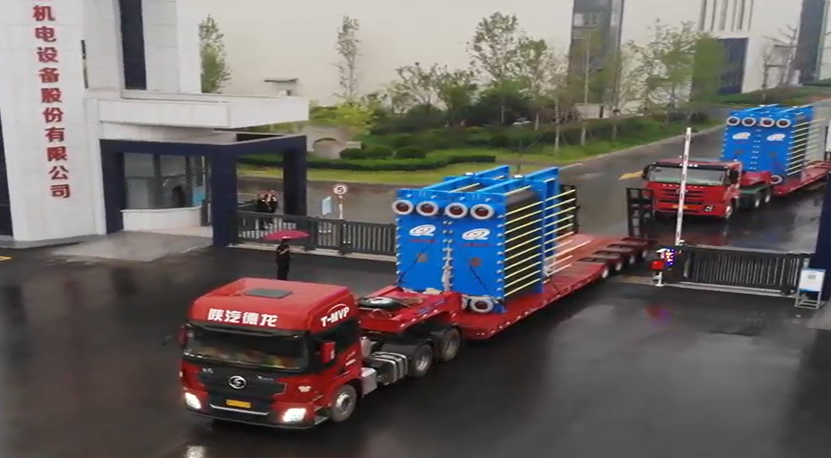
6.2.Transportation and Installation
Transport to the installation site according to user requirements and provide installation guidance and technical support.

7.Summary
The production process of plate heat exchangers involves precise plate processing, high-quality sealing gasket manufacturing, reliable frame design and strict quality inspection. Each step is crucial to the performance and durability of the equipment. This fine-craftsmanship and compact structure equipment provides reliable guarantee for efficient heat exchange in various industries.