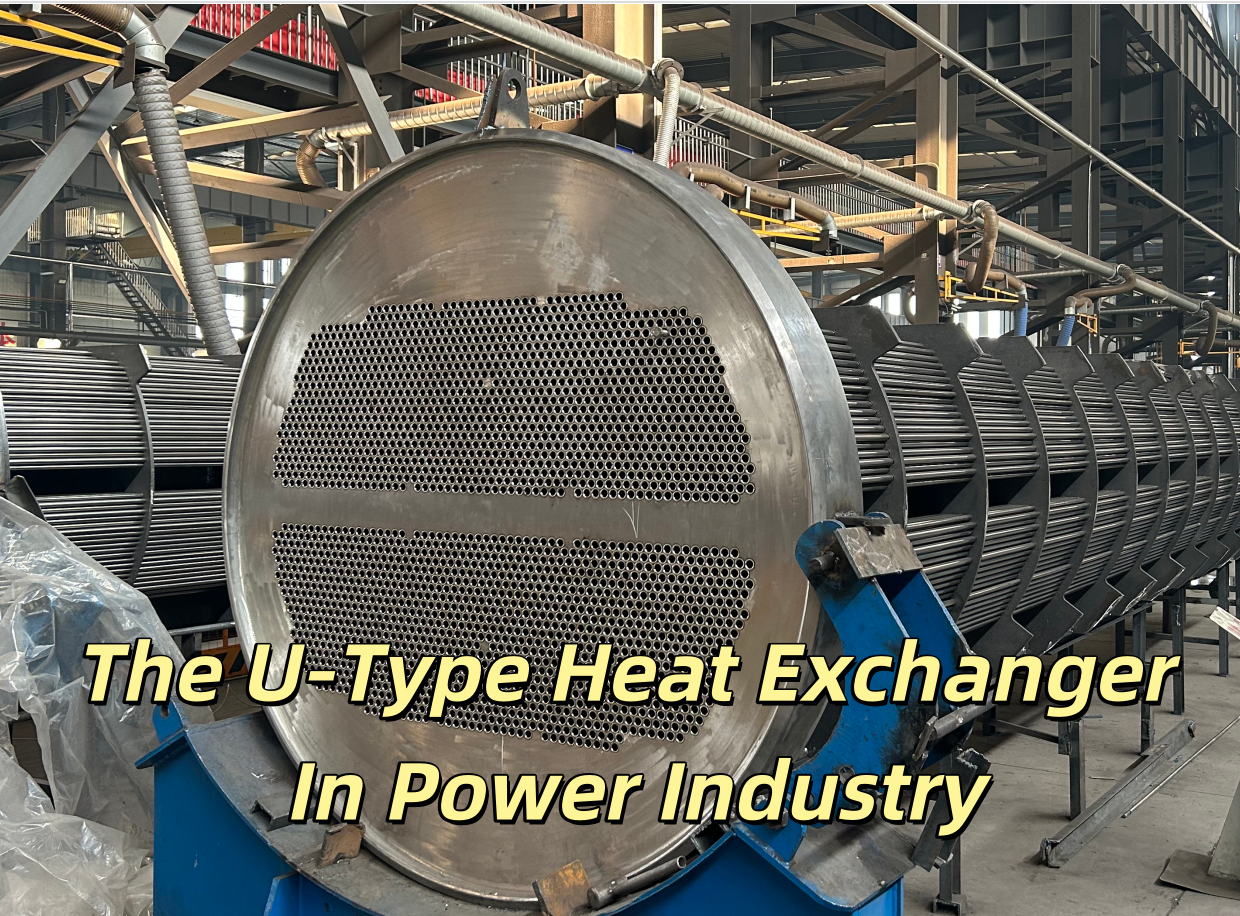
The application of U-tube heat exchangers in the power industry
Release time:
2025-06-13
The U-tube heat exchanger, due to its characteristics of withstanding high pressure and resisting thermal stress, is widely used in the power system in the following scenarios:


|
Scenario |
Typical System |
Functional Requirement |
|
Nuclear Power Plant |
Secondary Side System of Steam Generator (SG) |
Heat exchange between the primary loop and the secondary loop, with a pressure bearing > 15 MPa |
|
Thermal Power Plant |
Boiler Feedwater Preheating System |
Recover flue gas waste heat and increase thermal efficiency by 15 - 25% |
|
Gas Turbine Combined Cycle |
Condensate Heating of Heat Recovery Steam Generator (HRSG) |
Reduce exhaust gas temperature (< 90°C) and reduce heat pollution |
|
Geothermal Power Generation |
Geothermal Fluid - Working Fluid Heat Exchange |
Corrosion resistance (in H₂S/CO₂ environment) |
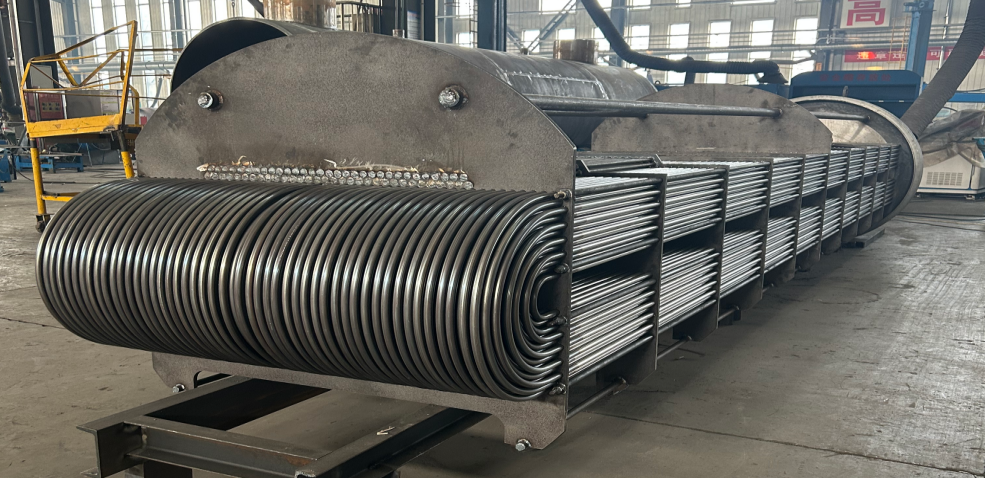

Technical advantages and design features
Structural Advantage
U-shaped tube bundle: One-sided free expansion design, eliminating temperature difference stress (applicable to working conditions with ΔT > 200℃), avoiding the risk of tube plate cracking.
Sealing: The tube pass and shell pass are completely isolated, suitable for the strict isolation requirements of the primary circuit (radioactive medium) and secondary circuit (clean water) in nuclear power plants.
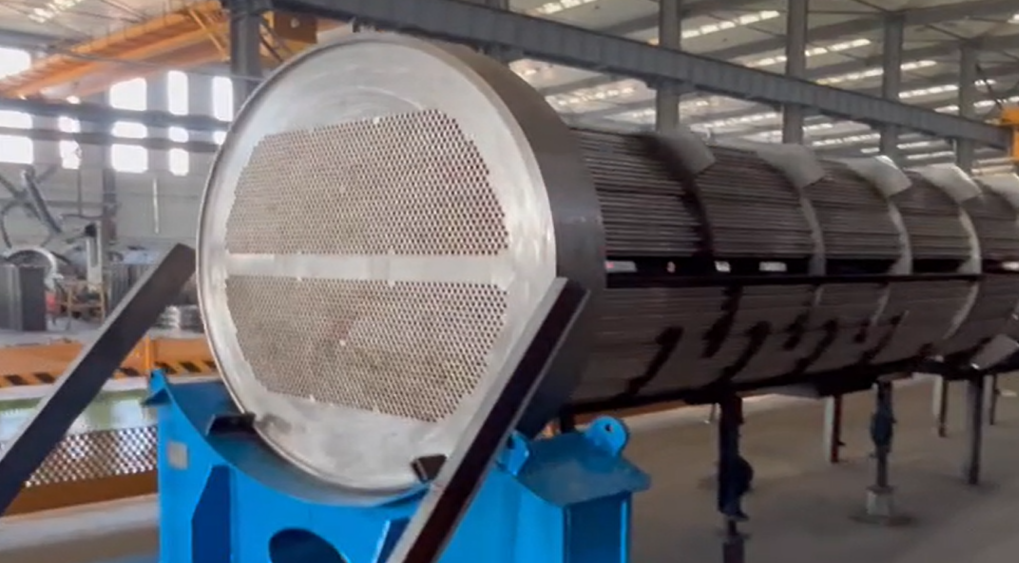

Material Selection
Nuclear power grade: Inconel 690 alloy tube (resistant to intergranular corrosion), designed for a lifespan of 60 years.
Thermal power grade: SA-213 T91 steel (resistant to 600°C high temperature), or titanium tube (for preventing salt fog corrosion in coastal power plants).
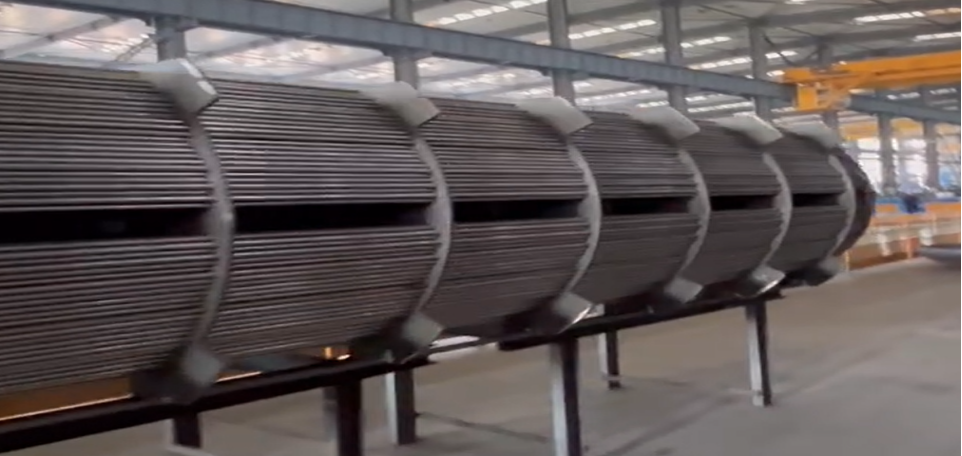

High-efficiency heat transfer
Shell-side turbulent flow design (optimization of baffle spacing) enables a heat transfer coefficient of up to 5000 W/(m²·K), which is 30% higher than that of the fixed tube sheet type.
Related Links:
Piping of shell and tube heat exchangers
The differences between PHV and Shell and Tube heat exchanger
How Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger Work