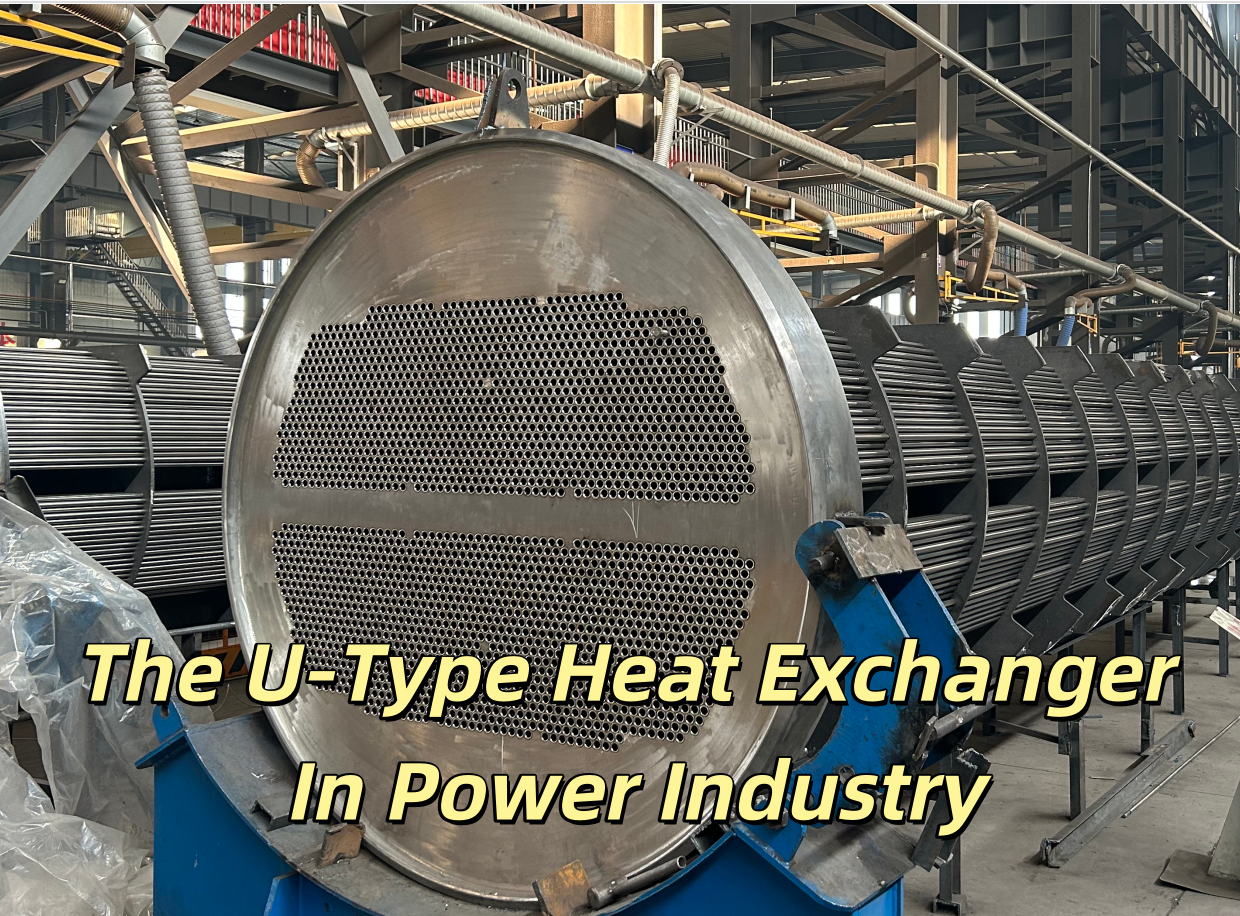
Welded plate heat exchanger plates
Release time:
2025-05-09
When welding the plates of a plate heat exchanger with a machine, special attention should be paid to the following key matters to ensure the welding quality, sealing performance and equipment service life:

1.Materials and surface treatment
Material matching: Confirm that the welding material is compatible with the plate material (such as stainless steel, titanium alloy, etc.) to avoid deformation or cracking caused by differences in thermal expansion coefficients.
Cleanliness: Thoroughly remove oil stains, oxides or impurities from the welding area. If necessary, use acetone or a dedicated cleaning agent to prevent porosity or false welding.
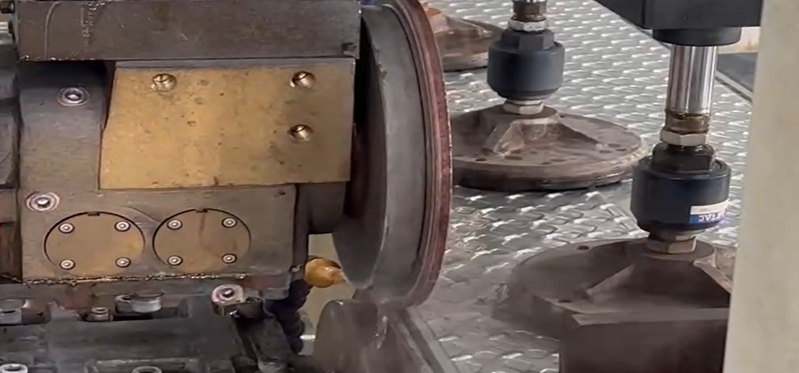
2.Welding process control
Parameter optimization: Precisely set the current, voltage and welding speed according to the thickness of the plate (usually 0.5-1.2mm) to avoid overburning or incomplete fusion (for example, TIG welding is recommended for stainless steel, with a current of 60-100A).
Heat input management: Pulse welding or section welding is adopted to control the heat input to reduce deformation (when welding thin plates, the deformation should be controlled within 0.1mm/m).
Protective gas: Use high-purity argon gas (≥99.99%) to protect the molten pool and prevent oxidation (especially for active metals such as stainless steel and titanium alloy).

3.Structure and Tooling design
Fixture positioning: Use a dedicated fixture to fix the flat plate to ensure alignment accuracy (usually requiring a parallelism error of less than 0.05mm).
Weld design: Lap welding or laser deep penetration welding should be given priority to ensure that the weld depth is ≥ 1.5 times the plate thickness to prevent leakage of the flowing medium.
Heat dissipation measures: Cover the non-welded areas with copper gaskets or water-cooling devices to reduce the heat-affected zone range (HAZ width is recommended to be less than 2mm).
4.Quality inspection and post-treatment
Non-destructive testing: Immediately after the welding is completed, conduct penetrant testing (PT) or X-ray inspection to identify microcracks (the allowable defect size must comply with ASME or GB standards).
Pressure test: Conduct a water pressure test at 1.5 times the working pressure (maintain pressure for 30 minutes) to confirm the sealing performance.
Stress relief: Perform local annealing treatment on high-stress areas (such as weld intersections) (for stainless steel, annealing at 650-800℃ is recommended).

5.Safety and Operation norms
Personnel protection: Operators must wear automatic light-changing welding masks and high-temperature resistant gloves to prevent arc burns and metal splashes.
Environmental control: The welding area should be well-ventilated and dusted to prevent the risk of metal dust explosion (concentration < 20g/m³).
Common Problem Responses
Deformation compensation: If local warping is found, flame correction method (heating temperature not exceeding 600℃) or mechanical leveling can be adopted.
Corrosion protection: Perform pickling and passivation treatment on stainless steel welds (nitric acid concentration 20%+ hydrofluoric acid 5%, temperature 50℃) to restore corrosion resistance.
Related Links:
How to install the rubber rings between the plates?
The process of PHE's flat plate opening and transverse shear