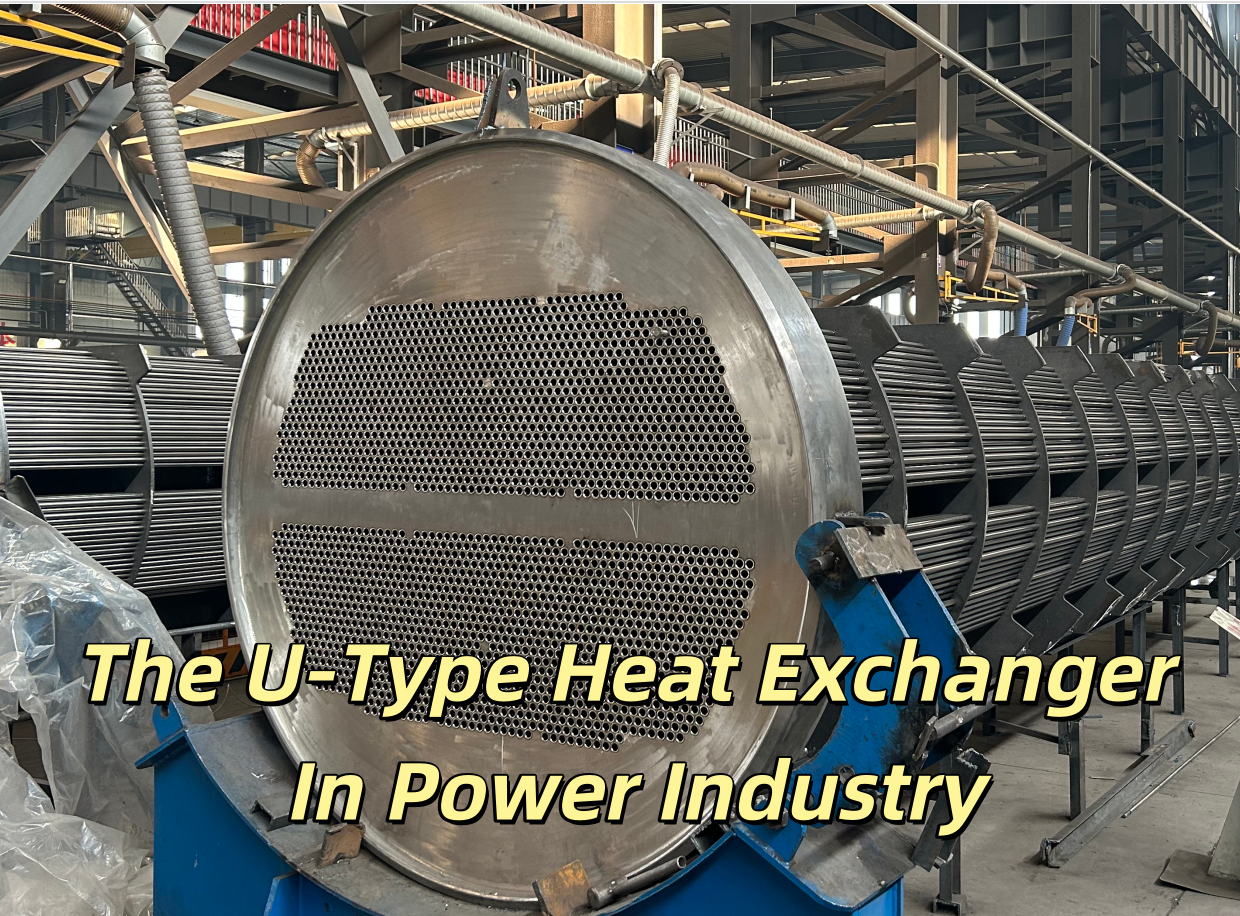
Plate heat exchanger working principle
Release time:
2025-02-05
Plate heat exchanger, as an efficient and compact heat exchange equipment, is widely used in various industrial fields, such as chemical, petroleum, food, pharmaceutical and so on. Its core function is to achieve heat transfer between two or more fluids to achieve heating, cooling or condensation. In this paper, the working principle of plate heat exchanger is deeply discussed from the aspects of structure and heat transfer characteristics, and the secret of efficient heat transfer is revealed.

1. The basic structure of plate heat exchanger
Plate heat exchangers consist of a series of corrugated metal sheets superimposed to form narrow channels between them for fluid to pass through. The corrugated design of the plate not only increases the degree of turbulence of the fluid, improves the heat exchange efficiency, but also enhances the strength and rigidity of the plate. In addition, the plates are sealed with rubber gaskets to ensure that the fluid does not leak into the external environment.
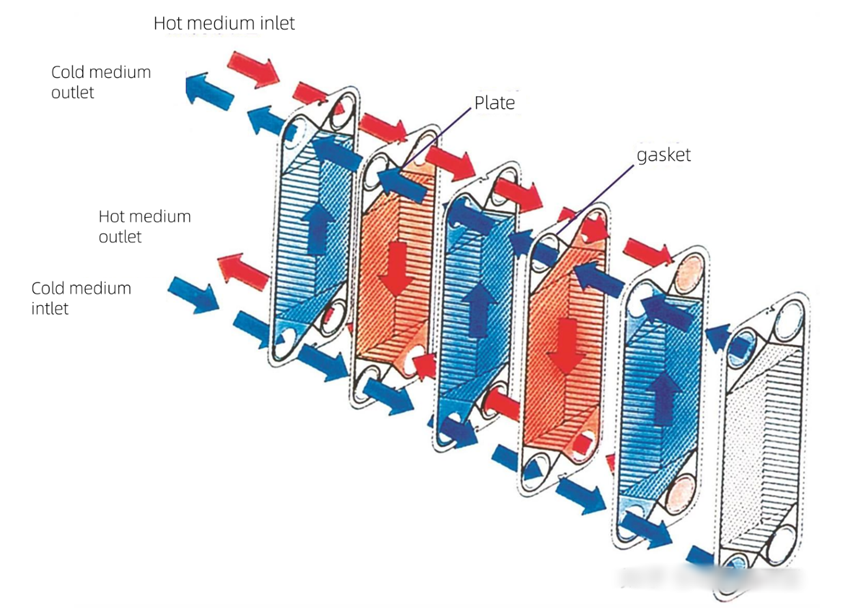
2. Working principle of plate heat exchanger
The working principle of plate heat exchanger is based on two heat exchange methods: heat conduction and convection. When two or more fluids with different temperatures flow through the channels between the plates, heat is transferred from the high temperature fluid to the low temperature fluid due to the temperature difference. In this process, the corrugated plate structure plays a key role, which increases the contact area between the fluid and the plate, while promoting the turbulence of the fluid, thereby improving the heat exchange efficiency.
The specific working principle mainly includes the following four aspects: fluid flow, heat conduction, convection heat transfer, as well as sealing and isolation.
Fluid flow: In plate heat exchangers, two fluids flow through different channels and do not mix with each other. High temperature fluids release heat during flow, while low temperature fluids absorb this heat, thus achieving heat transfer.
Heat transfer: Heat is transferred through the plate from a hot fluid to a cold fluid. Because the sheet material usually has good thermal conductivity, heat can be transferred quickly and efficiently.
Convective heat transfer: Convective heat transfer between the fluid and the plate is enhanced by the wavy design, which increases the degree of turbulence of the fluid as it flows through the channels between the plates. This enhanced convective heat transfer helps to further improve heat exchange efficiency.
Sealing and isolation: Plate heat exchangers are sealed between plates through rubber gaskets to ensure that fluid does not leak into the external environment. At the same time, this sealing structure also plays a role in isolating different fluids, preventing them from mixing with each other.